PRODUCTS

Add:No. 58 Fangbei Rd, Shijiazhuang 050011, Hebei province, China
Tel:+86 311 85319106
+86 13703116356
Fax:+86 311 68090963
Mail:hbkctc@sina.com
Technical overview of 5 types of stainless castings
There are five categories of stainless steel processing technology in stainless steel casting:
(1) The structure centered cubic (BCC) of martensitic stainless steel is attracted by the magnet, the quench temperature from the Austin magnetic field, and the best corrosion resistance, but the material is difficult and fragile, so ductile when tempered. However, when the resistance to corrosion is reduced, especially when tempered between 450 and 650 degrees, there are gaps in the carbon atom diffusion lattice and the precipitation of chromium carbide formed by the network of chromium carbides causes localized Consumption reduces the composition of the elemental chromium and makes it impossible to form a protection. Special care is needed as the film loses its corrosion resistance. The heat treatment temperatures of various stainless steel products are as follows.
(2) Ferritic stainless steel: This stainless steel valve body's central cubic structure (BCC) can attract magnets and is usually used in the automotive or chemical industry.
(3) Austenitic stainless steel: The central cubic structure (FCC) of the end face of this stainless steel does not affect the magnet and this material is easy to process. Therefore, different heat treatments can eliminate residual stresses in the processed material.
(4) Precipitation hardening type stainless steel: After high temperature hardening and low temperature heat treatment, this kind of stainless steel has strength or hardness because aluminum or copper element is precipitated along the sliding surface of the differential train or along the grain boundaries. Increase Commonly used precipitation hardening stainless steels include 17-4ph, 17-7ph, ph15-7mo, am-350, am-355.
(5) Post-welding heat treatment of various stainless steels: Chromium, an element contained in stainless steels, after welding, the high temperature region (haz) tends to disperse and bond to chromium carbides, carbides and become a local component. Unable to form a protective film, perforation Often corrosion occurs in the heat affected zone and can save the situation. After welding, the object is heat treated, the effect of which can be spread to other areas of the chrome and chrome deficient areas to achieve protection.
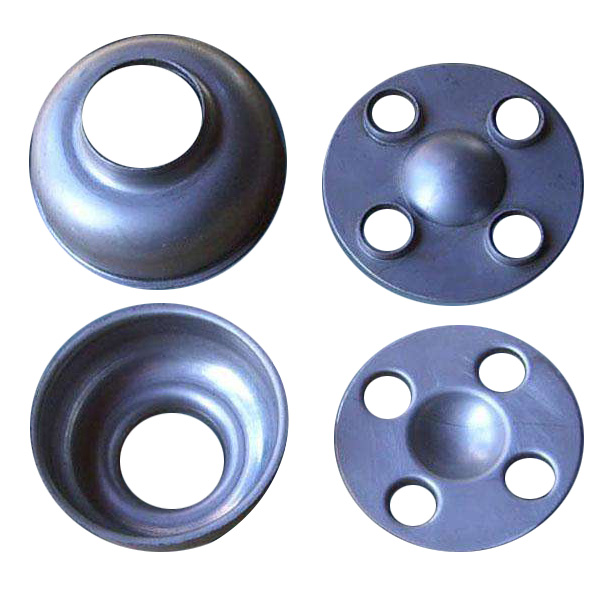
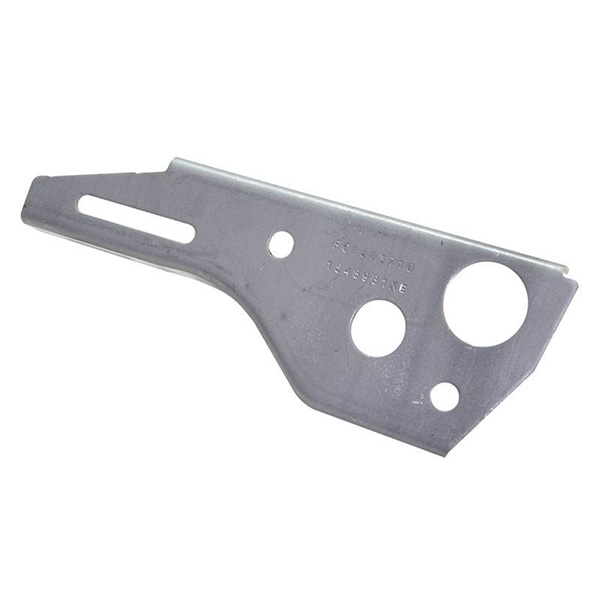
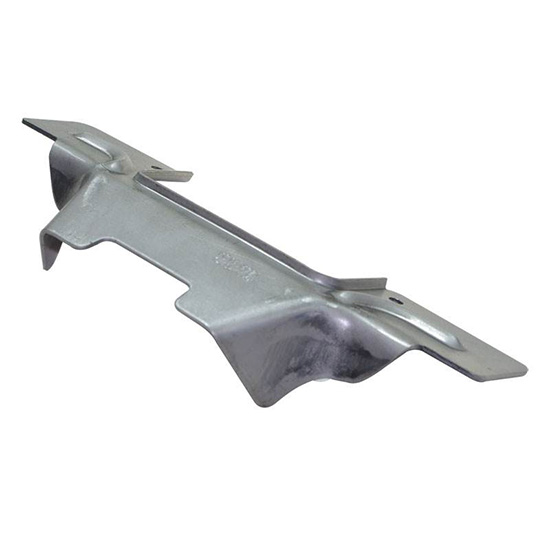





 Add:No. 58 Fangbei Rd, Shijiazhuang
050011, Hebei province, China
Add:No. 58 Fangbei Rd, Shijiazhuang
050011, Hebei province, China Tel: +86 311 85319106
Tel: +86 311 85319106  Mail:
Mail: